Maintaining accurate inventory is the backbone of any successful supply chain operation. Yet, traditional methods often fall short of meeting the demands of modern businesses. Enter cycle counting—a smarter, more efficient solution to inventory management challenges.
Cycle counting is a proactive inventory management technique that involves regularly counting small samples of inventory. Unlike traditional physical inventory counts, cycle counting ensures accuracy without disrupting daily operations. This approach helps businesses maintain reliable inventory records, reduce operational disruptions, and prevent costly stockouts.
In this article, we’ll explore the most effective cycle counting methods, their key benefits, and best practices for implementing a program that supports seamless and accurate inventory management.
Key Takeaways
- Minimized Disruptions: Cycle counting offers a flexible solution to maintaining accurate stock levels without halting daily operations, reducing stockouts and inaccuracies.
- Enhanced Inventory Control: Prioritizing high-value or fast-moving items through cycle counting improves overall inventory accuracy and operational efficiency.
- Technology Integration: Leveraging tools like barcode scanners and RFID systems streamlines the process, reduces errors, and ensures real-time data synchronization for effective inventory management.
Smarter Warehouse Management Starts Here
ASCTrac WMS delivers real-time visibility, automated workflows, and seamless ERP integration for warehouses of every size.
Request a Demo
Understanding Cycle Counting: A Smarter Approach to Inventory Management
Cycle counting is a proactive inventory management technique that ensures accurate stock levels by regularly counting small, targeted samples of inventory. This approach helps businesses maintain up-to-date records without interrupting daily operations.
A well-executed cycle counting program can identify discrepancies caused by shrinkage, data entry errors, or damaged items. By addressing these issues promptly, supply chain managers can maintain reliable inventory records and make informed decisions.
The key to successful cycle counting lies in its adaptability. By focusing on manageable subsets of SKUs, businesses can prioritize high-value or high-turnover items, maximizing accuracy and minimizing costs.
Cycle Counting vs. Physical Inventory Counts
Traditional physical inventory counts require halting operations to count all items at once, often leading to significant disruptions. In contrast, cycle counting offers a more flexible, efficient alternative by breaking the process into smaller, manageable counts conducted regularly.
Physical inventory counts are also more prone to human error due to the volume of items handled at one time. By targeting high-value or fast-moving SKUs, cycle counting ensures higher accuracy in inventory records while keeping operations running smoothly.
For supply chain leaders, cycle counting’s continuous approach helps address inventory shortages proactively, maintain real-time stock accuracy, and reduce costs—making it a preferred choice over traditional methods.

Key Benefits of Cycle Counting
Implementing cycle counting as part of your inventory management strategy offers significant benefits, helping supply chain leaders achieve greater operational efficiency and accuracy. Here’s how cycle counting can make a difference:
1. Improved Inventory Accuracy
Cycle counting is instrumental in reducing discrepancies between physical inventory and recorded data. Regular checks allow businesses to detect and resolve errors quickly, ensuring reliable inventory records.
With accurate inventory data, managers can make informed decisions, avoid overstocking or understocking, and streamline procurement processes. By integrating automation tools such as barcode scanners or RFID systems, the cycle counting process becomes even more precise, further minimizing errors.
2. Reduced Operational Disruptions
Unlike full physical inventory counts, which often require halting operations, cycle counting seamlessly integrates into daily workflows. By scheduling smaller, manageable counts, businesses can maintain accurate stock levels without compromising productivity.
This approach is particularly beneficial for high-demand environments, where operational downtime can result in significant revenue loss. Cycle counting ensures ongoing operations while keeping inventory data reliable and up-to-date.
3. Enhanced Inventory Control
Cycle counting enables managers to prioritize high-value or fast-moving items, ensuring these critical assets are always accurately tracked. By tailoring the process to focus on priority SKUs, businesses can improve inventory control and customer satisfaction.
For example, supply chain leaders can use cycle counting to verify the availability of top-selling products or items crucial to seasonal demand, ensuring smooth order fulfillment and reducing delays.
With these benefits in mind, let’s explore the methods that make cycle counting adaptable to your business needs. By choosing the right approach, supply chain leaders can further enhance efficiency and accuracy.
Common Cycle Counting Methods
Choosing the right cycle counting method is essential to achieving inventory accuracy and operational efficiency. Each method has its own advantages and is tailored to specific business needs. Below are three commonly used cycle counting techniques, along with insights to help you decide which might work best for your operations.
1. ABC Cycle Counting
The ABC cycle counting method prioritizes inventory based on the value or importance of items, categorizing them into three groups:
- A Items: High-value products that account for a significant portion of revenue or inventory costs. These items are counted most frequently.
- B Items: Mid-value products with moderate sales impact, counted periodically.
- C Items: Low-value or slow-moving items that are counted less often.
This method follows the Pareto principle, where approximately 20% of items drive 80% of the value. By focusing on A items more frequently, managers can ensure the accuracy of the most critical inventory, streamlining decision-making for high-revenue products.
ABC Cycle Counting:
| Category | Description | Counting Frequency |
| A Items | High-value items driving 80% of revenue or costs | Count frequently (e.g., weekly) |
| B Items | Mid-value items with moderate impact | Count periodically (e.g., monthly) |
| C Items | Low-value or slow-moving items | Count less often (e.g., quarterly) |
2. Random Sample Cycle Counting
Random sample cycle counting involves selecting items at random for inventory checks. This method can use two approaches:
- Constant Population Counting: The same number of items is counted during each cycle, randomly selected each time.
- Diminished Population Counting: Items are excluded from the sample once counted until the entire inventory has been checked.
Random sample cycle counting offers flexibility and reduces operational disruptions, making it ideal for organizations seeking to maintain inventory accuracy without overburdening staff. By ensuring all inventory has an equal chance of being counted, this method provides a balanced approach to inventory management.
3. Control Group Cycle Counting
Control group cycle counting involves repeatedly counting a small group of items to identify and resolve discrepancies. This method is particularly useful for refining processes and uncovering errors in inventory management.
For example, if consistent variances are detected in the control group, managers can investigate and address underlying issues, such as procedural gaps or training needs. Once the process is validated, the refined approach can be scaled to the broader inventory for improved accuracy and control.

Implementing a Cycle Counting Program
A successful cycle counting program requires a clear strategy and consistent execution. By following these steps, supply chain managers can integrate cycle counting seamlessly into their operations:
1. Review and Prepare Inventory Records
Start by ensuring your inventory records are accurate and up-to-date. Identify and correct discrepancies from previous counts or data entry errors before launching a cycle counting program. A solid foundation minimizes errors and streamlines future counts.
2. Plan the Cycle Counting Process
Create a structured plan that includes:
- Cycle Frequency: Determine how often counts should occur based on item value, turnover rates, and operational needs.
- Method Selection: Choose the most suitable counting method (e.g., ABC, random sample, or control group).
- Resource Allocation: Assign trained staff or use automated tools to ensure accuracy and consistency.
Planning ensures that the program aligns with business goals and minimizes operational disruptions.
3. Establish Policies and Procedures
Document your cycle counting policies to maintain consistency. These should cover:
- How to handle discrepancies.
- Steps for recording and reconciling inventory counts.
- Guidelines for prioritizing high-value or critical SKUs.
A clear framework allows staff to perform counts efficiently and with confidence.
4. Train Your Team
Proper training is essential for successful implementation. Equip your team with the knowledge and tools needed for accurate counting, including the use of barcode scanners or RFID systems. Emphasize the importance of following procedures and resolving variances.
5. Schedule Counts Strategically
Plan cycle counts during low-activity periods to avoid disrupting daily operations. For multi-location businesses, synchronize schedules across sites to ensure consistency. Regular scheduling keeps inventory records accurate and up-to-date.
6. Monitor and Adjust the Program
Regularly review cycle counting results to identify trends, discrepancies, or areas for improvement. Adjust the program as needed to address operational challenges, such as staffing shortages or unexpected inventory variances.
Best Practices for Cycle Counting
To maximize the efficiency and accuracy of your cycle counting program, it’s essential to follow proven best practices. These strategies help streamline operations, reduce errors, and ensure that inventory records remain reliable.
1. Regular Training and Updates
Continuous staff training is critical to maintaining consistency and accuracy in cycle counting. Provide clear instructions on counting procedures, handling discrepancies, and using technology like barcode scanners or RFID systems.
Regular updates ensure employees stay current with the latest tools and methods. A well-trained team minimizes errors and boosts confidence in the accuracy of inventory data.
2. Leverage Technology for Efficiency
Modern inventory management tools, such as handheld barcode scanners and RFID systems, significantly enhance the cycle counting process. These technologies:
- Reduce manual errors.
- Provide real-time data synchronization.
- Speed up the counting process, allowing teams to focus on higher-priority tasks.
Integrating these tools into your cycle counting program not only improves accuracy but also saves time and resources.
3. Prioritize High-Value or Fast-Moving Items
Focusing on critical SKUs—such as high-value or fast-moving items—ensures that your inventory’s most impactful assets are consistently accurate. Use methods like ABC cycle counting to prioritize these items, minimizing stockouts and overstocking.
By targeting high-priority items, businesses can maximize the overall impact of their cycle counting efforts.
4. Analyze and Refine Processes
Cycle counting is not a static process—it requires regular analysis to identify patterns and areas for improvement. Monitor results to spot recurring discrepancies or inefficiencies, and adjust procedures accordingly.
For example, if certain SKUs consistently show variances, investigate root causes like shrinkage or procedural errors. Refining processes over time ensures continuous improvement in inventory accuracy.

Challenges and Solutions in Cycle Counting
While cycle counting offers numerous benefits, it is not without challenges. Addressing these obstacles effectively ensures the program’s success and helps maintain accurate inventory records.
1. Handling Inventory Discrepancies
Challenge: Discrepancies in inventory records, caused by factors like shrinkage, data entry errors, or damaged items, can impact decision-making and operational efficiency.
Solution: Investigate and resolve discrepancies promptly. Use cycle counting data to identify patterns, such as recurring variances in specific SKUs or locations. Implement corrective measures, like better staff training or enhanced security, to reduce discrepancies in the future.
2. Managing Multi-Location Inventories
Challenge: Maintaining consistency and accuracy across multiple warehouse locations introduces complexity, particularly when dealing with paperwork delays or unrecorded transactions.
Solution: Standardize cycle counting procedures across all locations and synchronize inventory data in real-time using a warehouse management system (WMS). Assign dedicated staff to oversee cycle counts at each site, ensuring accountability and consistency.
3. Reducing Human Error
Challenge: Manual processes can lead to counting mistakes, especially in high-volume operations.
Solution: Leverage automation tools like barcode scanners, RFID systems, and inventory management software to minimize manual errors. Provide training to ensure staff can effectively use these technologies and follow standardized procedures.
4. Scheduling Challenges
Challenge: Unexpected operational interruptions or lack of staff availability can disrupt scheduled cycle counts.
Solution: Plan cycle counting during low-activity periods to minimize disruptions. Use automated scheduling features within your WMS to ensure counts are conducted consistently. Flexibility in scheduling can also help accommodate unforeseen challenges.
The Role of Automation in Cycle Counting
Automation plays a pivotal role in enhancing the accuracy, efficiency, and scalability of cycle counting programs. By reducing reliance on manual processes, businesses can streamline operations and achieve higher inventory accuracy.
Benefits of Automated Systems
Implementing automation tools in cycle counting offers several advantages:
- Reduced Errors: Automation minimizes human error during inventory checks, ensuring more accurate records.
- Improved Efficiency: Technologies like barcode scanners and RFID systems enable faster counting, freeing staff for other critical tasks.
- Real-Time Updates: Automated systems synchronize inventory data instantly, reducing delays and providing managers with up-to-date insights.
For example, RFID technology can count inventory without the need for direct line-of-sight, making it ideal for high-density storage environments. Similarly, handheld barcode scanners allow for quick and accurate data capture, ensuring seamless integration with inventory systems.
Example of automated cycle counting system:
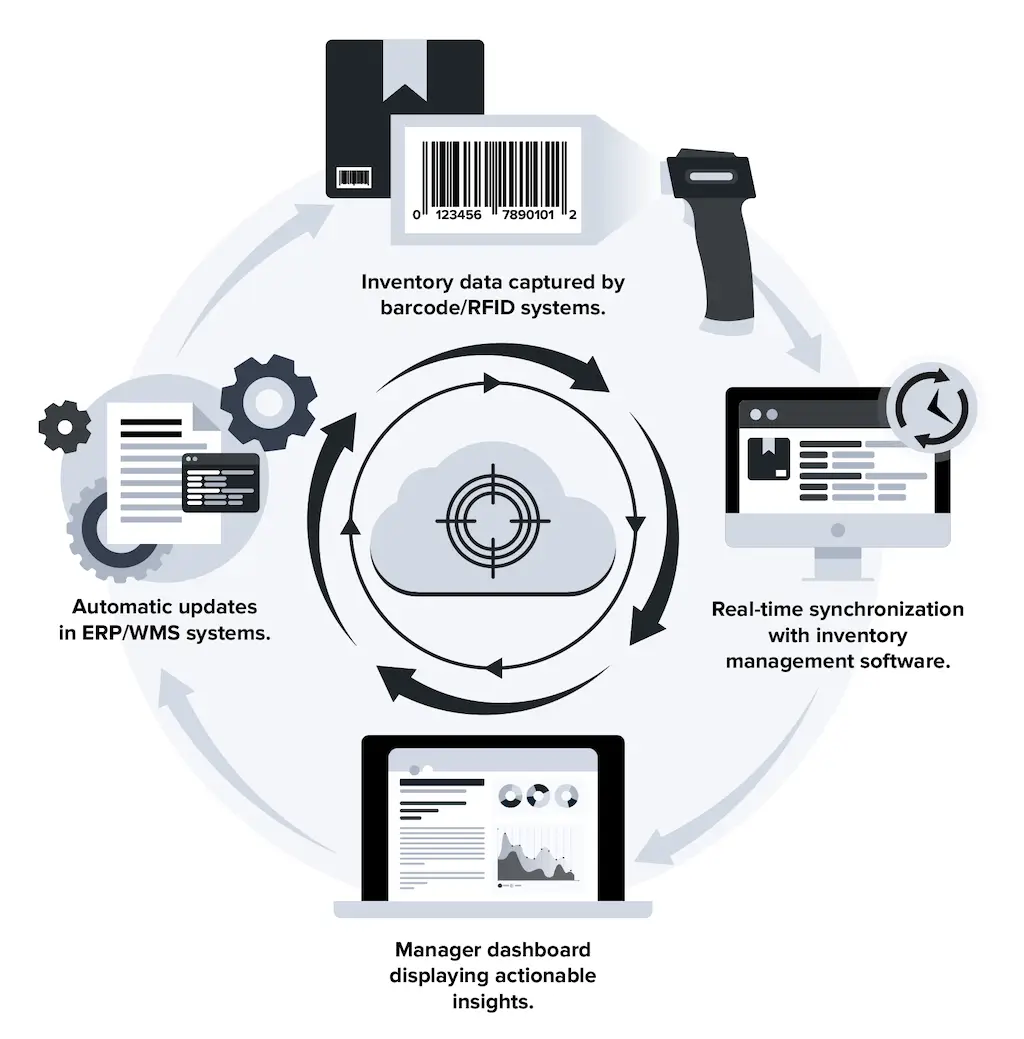
Popular Automation Tools
Several tools and technologies are commonly used in automated cycle counting:
- Barcode Scanners: Essential for capturing data efficiently and reducing manual input errors.
- RFID Systems: Allow for rapid, non-invasive inventory tracking, particularly in large warehouses.
- Inventory Management Software: Automates the scheduling, tracking, and reconciliation of cycle counts, ensuring consistency across locations.
By integrating these tools, businesses can optimize their cycle counting processes, improve data accuracy, and reduce operational disruptions.
Key Considerations for Implementation
When adopting automation for cycle counting, it’s essential to:
- Choose tools that integrate seamlessly with your existing inventory management system.
- Train staff to use these technologies effectively.
- Regularly monitor automated processes to ensure they meet operational goals and identify areas for improvement.

Integrating Cycle Counting with Inventory Management Systems
Integrating cycle counting into your inventory management system is key to maintaining accurate stock levels and streamlining operations. When combined with the right tools, this approach can transform inventory management from a reactive to a proactive process.
Why Integration Matters
A well-integrated inventory management system automates cycle counting processes, enabling:
- Real-Time Updates: Inventory records are instantly synchronized, reducing discrepancies and improving decision-making.
- Automated Scheduling: Systems can schedule cycle counts based on inventory parameters, such as turnover rates or item value, ensuring consistent coverage.
- Centralized Data Management: Consolidating inventory data across locations simplifies reporting and trend analysis.
For example, an ERP system with integrated cycle counting capabilities eliminates the need for manual tracking, ensuring consistent updates and accurate inventory records across all warehouse locations.
Choosing the Right System
When selecting an inventory management system to support cycle counting, look for features such as:
- Automated tracking and reporting.
- Seamless integration with existing ERP or WMS platforms.
- User-friendly interfaces for quick adoption by your team.
A system tailored to your operational needs not only enhances cycle counting but also improves overall inventory control.
Synchronizing Data for Accuracy
Synchronization ensures that all cycle counting data is reflected in your system immediately, reducing the risk of errors caused by delayed updates. By automating data synchronization, supply chain managers can:
- Identify discrepancies faster.
- Maintain accurate inventory records in real-time.
- Improve operational efficiency and inventory visibility.
ASC Software: Your Partner in Streamlining Cycle Counting and Inventory Management
Cycle counting becomes truly transformative when powered by advanced inventory management solutions. ASC Software offers a state-of-the-art Warehouse Management System (WMS) designed to enhance your cycle counting program and overall operational efficiency.
Key Features of ASC Software’s WMS:
- Automated Inventory Tracking: Eliminate manual errors with integrated tools like barcode scanners and RFID technology for real-time, precise data updates.
- Customizable Cycle Counting Options: Tailor cycle counting schedules, methods (ABC, random sample, or control group), and priorities to align with your business goals.
- Real-Time Data Synchronization: Maintain accurate inventory records across single or multiple locations with centralized reporting and analytics tools.
- Scalability for Growing Businesses: Whether managing one warehouse or multiple sites, ASC Software’s WMS adapts to your business, supporting seamless growth and consistent operations.
Why Choose ASC Software?
With ASC Software’s innovative solutions, your business can:
- Minimize operational disruptions.
- Enhance inventory accuracy and control.
- Streamline cycle counting processes for maximum efficiency.
Take the first step toward transforming your inventory management strategy. Contact us today to discover how ASC Software’s WMS can help your business achieve greater accuracy, efficiency, and scalability.
Summary
Cycle counting is an essential tool for maintaining accurate inventory levels while minimizing disruptions to daily operations. By implementing best practices, leveraging automation, and addressing common challenges, businesses can transform their inventory management processes.
Key benefits of cycle counting include:
- Improved inventory accuracy.
- Reduced operational disruptions.
- Enhanced inventory control for high-value and fast-moving items.
For supply chain leaders, the integration of cycle counting with inventory management systems ensures real-time data synchronization and streamlined operations. By prioritizing regular training, adopting automation tools, and refining processes, businesses can achieve greater efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Ready to elevate your inventory management? Contact ASC Software today to learn how our WMS can simplify your cycle counting process and enhance your operations.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is cycle counting?
Cycle counting is a proactive inventory management technique that involves regularly counting small samples of inventory to ensure accuracy. Unlike full physical inventory counts, cycle counting prevents operational disruptions by integrating seamlessly into daily workflows.
How does cycle counting differ from physical inventory counts?
Cycle counting focuses on smaller, more frequent counts, while physical inventory counts require stopping operations to count all items at once. This makes cycle counting less disruptive and more efficient for businesses with high turnover.
What are the main benefits of cycle counting?
Cycle counting improves inventory accuracy, reduces operational downtime, and enhances control over high-value or fast-moving items. With the use of technology, such as barcode scanners and RFID systems, the process becomes even more efficient and reliable.
How can automation enhance cycle counting?
Automation minimizes human error and streamlines the cycle counting process. Tools like barcode scanners and RFID systems ensure real-time data updates, while inventory management software schedules counts and reconciles discrepancies automatically.
Which cycle counting method is right for my business?
The best method depends on your operational priorities:
- ABC Cycle Counting: Ideal for businesses prioritizing high-value items.
- Random Sample Cycle Counting: Suitable for maintaining overall inventory accuracy with minimal disruptions.
- Control Group Cycle Counting: Best for identifying and addressing discrepancies in specific areas.




