Delve into the essentials of Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) and learn how they’re the key to unlocking efficiency and clarity in your warehouse operations.
Introduction to Warehouse Management Systems (WMS)
The Evolution of Warehouse Management
In the ever-evolving landscape of logistics and supply chain management, Warehouse Management Systems (WMS) have emerged as pivotal tools for businesses seeking efficiency and accuracy. The journey of WMS began in the 1970s, evolving from simple location and stock level management to sophisticated systems that now orchestrate a wide array of warehouse operations. Control Automation details how, “A WMS was first used by clothing retail company J.C. Penney in 1975, effectively starting the modern era of warehouse management.”
Today, WMS solutions are not just about storage optimization; they are integral components that drive the entire supply chain’s efficiency, from inventory control to order fulfillment.
As we delve into the world of WMS, it’s essential to understand how these systems have transformed warehouse operations. They have transitioned from basic manual processes to automated, data-driven solutions that offer real-time insights and analytics. This evolution has been fueled by technological advancements, changing market demands, and the continuous pursuit of operational excellence.
Understanding Warehouse Management Software
Defining WMS: More Than Just Storage Management
At its core, Warehouse Management Software is a tool designed to support and optimize warehouse functionality and distribution center management. These systems facilitate the management of inventory, streamline picking and packing processes, and improve the accuracy of order fulfillment. But what sets modern WMS systems apart is their ability to integrate seamlessly with other supply chain management systems, such as Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) and Supply Chain Management (SCM) software, thereby creating a cohesive and efficient operational flow.
The Role of a WMS in Modern Warehousing
In contemporary warehousing, a WMS is not just a tool but a strategic partner that helps businesses adapt to market changes, customer demands, and supply chain disruptions. It enables warehouses to maximize space utilization, reduce waste, and optimize labor management. By providing real-time data and insights, WMS systems empower decision-makers to make informed choices, anticipate challenges, and respond proactively to dynamic market conditions. Forbes notes, “The right intelligent software can help [warehouse managers] take that first step through digitization that will help them manage their SKU distribution and workflows.”
The integration capabilities of a WMS extend its impact beyond the warehouse. By connecting with procurement, sales, and transportation systems, a WMS ensures that every part of the supply chain is informed and synchronized. This interconnectedness is crucial in today’s fast-paced business environment, where any delay or miscommunication can significantly impact customer satisfaction and the bottom line.

Types of Warehouse Management Systems
Traditional vs. Modern WMS: A Comparative Look
Warehouse Management Systems have evolved significantly over the years, leading to a distinction between traditional and modern systems. A traditional WMS, often characterized by their on-premises deployment and focus on basic functionalities like storage location, have served warehouses well for basic operational needs. However, the advent of more complex supply chains has given rise to modern WMS solutions. These are typically cloud-based and offer a broader range of functionalities, including advanced analytics, real-time data processing, and integration with various supply chain management tools.
Cloud-Based vs. On-Premises Solutions
The debate between cloud-based and on-premises WMS solutions is central to the discussion of WMS types. Cloud-based WMS systems offer flexibility, scalability, and reduced IT overhead, making them attractive for businesses looking for cost-effective and agile solutions. On the other hand, on-premises systems provide a sense of control and security, particularly for businesses with highly specialized needs or those operating in industries with stringent data security regulations. The choice between these two depends on a variety of factors, including business size, budget, and specific operational requirements.
Key Features of an Effective WMS
Inventory Management: The Heart of a WMS
Effective inventory management is at the core of any WMS. It involves tracking stock levels, orders, and deliveries to optimize inventory holding and reduce costs associated with overstocking or stockouts. A robust WMS provides real-time visibility into inventory, enabling businesses to make quick decisions based on current market demands and inventory status. These are typically core WMS features although they may be included as part of inventory management modules.
Order Fulfillment and Processing: Ensuring Customer Satisfaction
A WMS streamlines the entire order fulfillment process, from order receipt to shipment. This includes automating picking and packing processes, which not only speeds up order processing but also reduces errors, ensuring that customers receive the right products on time. This aspect of a WMS is crucial in maintaining high levels of customer satisfaction and loyalty.
Labor Management: Optimizing Workforce Efficiency
Labor management in a WMS involves assigning the right tasks to the right employees at the right time, ensuring that the workforce is utilized efficiently. By tracking labor performance and productivity, a WMS can help identify areas for improvement and training, leading to a more efficient and effective workforce.
Integration with Other Systems: Creating a Cohesive Supply Chain
A key feature of an effective WMS is its ability to integrate with other systems such as enterprise resource planning (ERP), supply chain management (SCM), and transportation management systems (TMS). This integration ensures that data flows seamlessly across the supply chain, enhancing transparency and coordination among different departments and processes.
Advanced Reporting and Analytics: Driving Informed Decisions
Data-driven decision-making is powered by advanced reporting and analytics features. A WMS should provide detailed insights into warehouse operations, including inventory turnover, order fulfillment metrics, and labor productivity, enabling continuous improvement.
Flexible and Scalable Architecture: Adapting to Business Growth
An effective WMS must be both flexible and scalable, and be able to adapt to the changing needs of a business. This includes accommodating different operational sizes, varying inventory types, and expanding business requirements such as connecting multiple warehouses.
Enhanced Security and Compliance: Safeguarding Critical Data
Security and compliance features are critical, especially in industries with stringent regulatory requirements. A WMS should offer robust data security, audit trails, and compliance management tools.
Mobile and Wireless Capabilities: Empowering On-the-Go Operations
In today’s fast-paced environment, mobile and wireless capabilities in a WMS are indispensable. They allow for real-time data access and transactions from anywhere in the warehouse, increasing efficiency and flexibility.
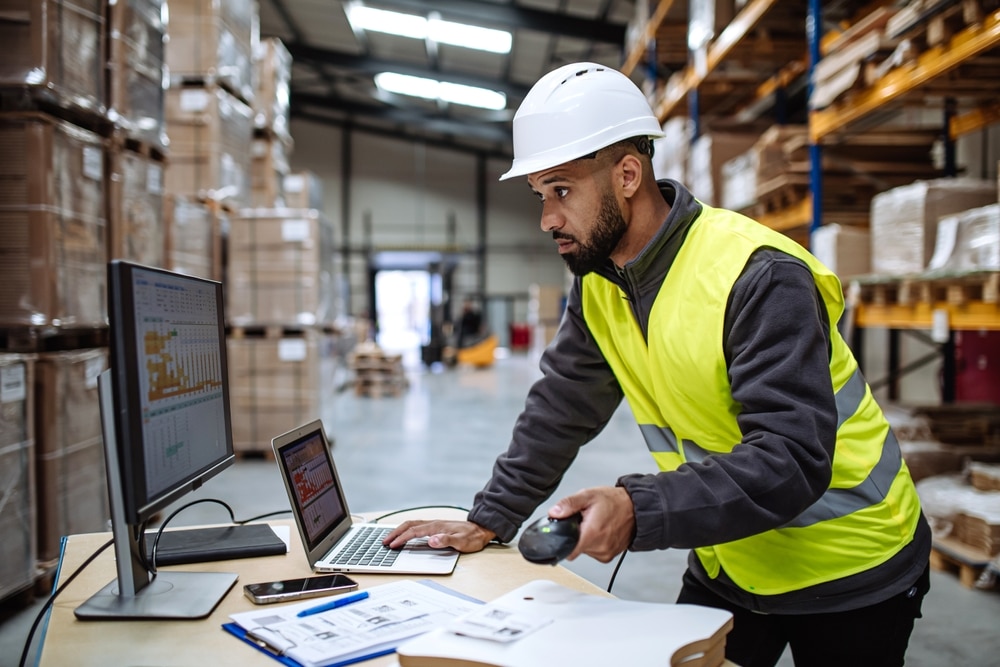

Harnessing Advanced Technologies with a WMS
Warehouse Management Systems today are increasingly incorporating advanced technologies to enhance efficiency and accuracy. While the extent of technology adoption varies across warehouses, certain innovations have made significant inroads in modernizing warehouse operations.
IoT, RF, and RFID: Revolutionizing Inventory Tracking
The integration of the Internet of Things (IoT), Radio-Frequency Identification (RFID), and RF scanning in WMS has been revolutionary for many warehouses. These technologies provide real-time tracking of inventory, offering a level of visibility and accuracy previously unattainable. Their adoption is a must for warehouses that prioritize real-time data and operational efficiency.
Voice-Picking and Pick-to-Light Systems: Streamlining Picking Processes
Voice-picking and pick-to-light systems are increasingly popular in warehouses looking to optimize their picking processes. By guiding workers more efficiently and reducing errors, these technologies significantly speed up order fulfillment and enhance overall productivity.
Automated Conveyors and AS/RS: Optimizing Product Movement
For warehouses dealing with high volumes of goods, automated conveyor systems and Automated Storage and Retrieval Systems (AS/RS) have become essential. These technologies automate the movement and storage of goods, improving throughput and reducing manual labor.
Robotics and AGVs: The Next Step in Automation
Robotics and Automated Guided Vehicles (AGVs) represent the next step in warehouse automation. While not present in all warehouses, automation technologies are increasingly adopted by companies such as General Mills for their ability to handle repetitive tasks, transport goods, and assist in picking, thereby enhancing operational efficiency.
While the technologies we’ve mentioned are currently reshaping many warehouse operations, it’s important to note that not all WMS solutions may include or integrate with all these innovations. However, understanding and considering these technologies is crucial for warehouses aiming to stay competitive and efficient.
Keep reading as we’ll explore future trends and emerging technologies, such as drones and Augmented Reality (AR), that are set to further transform warehouse management.

Warehouse Management Systems for Different Business Models
Tailoring WMS for Ecommerce
Ecommerce operations require WMS solutions that prioritize speed, accuracy, and scalability. These systems must efficiently handle high volumes of small orders, manage returns, and integrate with online sales platforms, ensuring customer satisfaction and fostering repeat business.
WMS in Manufacturing and Retail
In manufacturing, WMS systems align closely with production schedules to manage raw materials and finished goods effectively. In the retail sector, a WMS focuses on product availability, managing seasonal fluctuations, and integrating with point-of-sale systems, thereby enhancing operational efficiency and market responsiveness.
WMS for Third-Party Logistics (3PL)
WMS solutions for 3PL providers must offer robust inventory management, billing functionalities, and the ability to handle diverse client requirements, ensuring efficient operations across multiple clients with varying needs.
WMS for Pharmaceuticals
In the pharmaceutical industry, WMS solutions play a critical role in ensuring compliance with stringent regulatory standards, managing sensitive products, and maintaining accurate lot and serial number tracking for safety and traceability.
WMS for Food and Beverage
WMS solutions in the food and beverage sector must manage perishable goods, support lot traceability, and comply with health and safety regulations. Systems often include features for managing expiry dates and ensuring first-expired, first-out (FEFO) inventory rotation.
WMS for Wholesale Distribution
For wholesale distributors, a WMS needs to handle large volumes of products, manage complex supplier relationships, and efficiently process large orders for B2B transactions.
WMS for Manufacturing
Beyond traditional manufacturing, WMS also supports discrete and process manufacturing environments, where it needs to integrate tightly with manufacturing execution systems (MES) and material requirements planning (MRP) systems.
Adapting to Specific Needs
Each of these industries has unique requirements and challenges that a WMS must address. The ability of a system to adapt to the specific needs of different business models and industries is crucial for enhancing operational efficiency and meeting market demands.

Optimizing Operations: The Impact of WMS on Efficiency
Improving Order Accuracy and Efficiency
A key benefit of a Warehouse Management System is its ability to significantly improve order accuracy and efficiency. By automating processes such as picking and packing, and by providing real-time inventory data, WMS solutions minimize errors and speed up order processing. This leads to more accurate order fulfillment, which is crucial for maintaining customer trust and satisfaction.
Metrics and Analytics for Performance Tracking
Modern WMS solutions come equipped with robust analytics and reporting tools. These tools provide valuable insights into warehouse operations, allowing managers to track performance metrics such as order turnaround times, inventory turnover rates, and labor productivity. By analyzing this data, businesses can identify areas for improvement, make informed decisions, and continuously optimize their warehouse operations.
The Strategic Benefits a WMS Provides
Enhancing Productivity and Reducing Costs
Implementing a WMS can lead to significant productivity gains and cost reductions. By optimizing warehouse space, improving inventory accuracy, and streamlining processes, a WMS reduces waste and operational expenses. Additionally, the increased efficiency often leads to a reduction in labor costs and an overall improvement in the bottom line.
Gaining a Competitive Edge with WMS
In today’s fast-paced market, a WMS can provide businesses with a competitive advantage. By ensuring quick and accurate order fulfillment, maintaining optimal inventory levels, and adapting swiftly to market changes, the right WMS enables businesses to meet customer expectations consistently and efficiently. This responsiveness and reliability can set a business apart in a crowded marketplace.
Choosing the Right WMS: A Buyer’s Guide
Factors to Consider When Selecting a WMS
Choosing the right Warehouse Management System is crucial for maximizing its benefits. Key factors to consider include the system’s scalability, compatibility with existing technology, user-friendliness, and the specific features it offers. Additionally, the level of customer support provided by the vendor is essential, especially for businesses implementing a WMS for the first time.
Questions to Ask Vendors
When evaluating WMS vendors, it’s important to ask the right questions. Inquiries should cover areas such as the system’s integration capabilities, customization options, data security measures, and the vendor’s experience in your specific industry. Understanding the vendor’s approach to training and ongoing support is also vital for a successful implementation.
Market Overview: Vendors and Pricing Structures
Overview of WMS Vendors
The WMS market features a wide range of vendors, each offering solutions with different strengths and specializations. Some vendors cater to large, multinational corporations with complex supply chains, while others focus on small to medium-sized businesses. It’s important to understand the vendor landscape to find a solution that aligns with your business needs.
Understanding the Pricing Models
WMS pricing models vary significantly among vendors. Some common pricing structures include one-time licensing fees, subscription-based models, and pay-per-use arrangements. Businesses should consider the total cost of ownership, including implementation, customization, training, and support costs, when evaluating different pricing models. But don’t just look at the price tag alone; consider factors like improved efficiency, cost savings, current and future needs, and ROI.

Implementing a WMS: Best Practices and Challenges
Steps for Successful Implementation
Implementing a Warehouse Management System is a significant undertaking that requires careful planning and execution. Best practices include conducting a thorough needs analysis, involving key stakeholders in the planning process, and choosing a vendor that offers robust support and training. It’s also crucial to have a detailed implementation plan that includes data migration, system testing, and user training.
Overcoming Common Implementation Challenges
Common challenges during WMS implementation include managing change within the organization, ensuring data accuracy, and integrating the WMS with existing systems. Overcoming these challenges requires clear communication, comprehensive training programs, and possibly phased implementation strategies to ensure a smooth transition.
Future Trends in Warehouse Management Systems: Preparing for Tomorrow
Predictions and Emerging Innovations
The future of Warehouse Management Systems is likely to be shaped by continued technological advancements. Trends to watch include the increased use of AI and machine learning for predictive analytics, greater integration with IoT devices for enhanced real-time tracking, further developments with drones, automation and robotics, and the adoption of augmented reality (AR) for training and operational purposes. Additionally, the rise of sustainable and green warehousing practices may influence future WMS developments.
ASC Software’s WMS: Streamlining Your Warehouse Operations
ASC Software’s Warehouse Management System is crafted to directly address the operational needs of modern warehouses, offering a suite of features that bring efficiency, accuracy, and cost-effectiveness to your business.
Core Features and Benefits:
- Real-Time Inventory Management: Gain accurate, real-time insights into inventory levels and movements, reducing errors and optimizing stock control.
- Streamlined Order Processing: Automated order processing accelerates fulfillment, enhances customer satisfaction, and supports higher order volumes.
- Efficient Labor Management: Maximize workforce productivity with optimized task allocation and performance tracking.
- Seamless System Integration: Easily integrate with existing ERP, SCM, and eCommerce platforms, along with EDI and API integrations for cohesive operations and data consistency.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Leverage advanced analytics for strategic insights into warehouse performance, driving continuous improvement.
- User-Friendly Interface: Benefit from an intuitive interface that simplifies complex operations, enhancing user adoption and efficiency.
- Scalable Solution: Our WMS grows with your business, ensuring a future-proof investment that adapts to expanding operational needs.
- Robust Support and Training: Receive comprehensive training and ongoing support for a smooth transition and sustained operational success.
Empower Your Warehouse with ASC Software
With ASC Software’s WMS, elevate your warehouse operations to new levels of operational excellence, ensuring your business is equipped for both current challenges and future growth.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we’ve explored the vital role of Warehouse Management Systems in modern logistics and supply chain management. From the evolution of early WMS solutions to the integration of advanced technologies, we’ve seen how these systems enhance inventory management, streamline order processing, and optimize labor efficiency. We’ve also discussed how WMS solutions are tailored for various industries, ensuring operational excellence across diverse business models.
ASC Software’s WMS stands at the forefront of this evolution, offering a solution that not only meets today’s warehouse management challenges but also scales for tomorrow’s opportunities. Our system is designed for businesses seeking to enhance efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in their warehouse operations.
Ready to transform your warehouse operations? Contact ASC Software to discover how our innovative WMS can elevate your business to new heights of operational excellence.
Explore ASC Software’s WMS – Your gateway to a more efficient and productive warehouse.
FAQs About Warehouse Management Systems
What does a warehouse management system do?
A Warehouse Management System (WMS) orchestrates various warehouse operations, from tracking inventory and managing orders to optimizing the picking and shipping processes. It enhances efficiency, accuracy, and productivity in warehouse management.
What software is used for warehouse management?
Warehouse management typically utilizes specialized WMS software. These systems offer tools for inventory control, order processing, labor management, and integration with other supply chain management systems, like ERP and SCM.
What is WMS system software?
WMS system software, or Warehouse Management System software, is designed to support and optimize the functionality of warehouses and distribution centers. It streamlines operations, improves inventory accuracy, and enhances order fulfillment processes.
What is warehouse inventory management software?
Warehouse inventory management software is typically a component of a WMS that is focused on managing the storage, movement, and tracking of inventory within a warehouse. It ensures optimal stock levels, reduces costs associated with inventory mismanagement, and provides real-time visibility.
What software is used for inventory management?
Inventory management in warehouses is often handled by a WMS, which includes specific modules for inventory control. These modules track stock levels, manage orders, and assist in forecasting demand, ensuring efficient inventory management.
How do you manage inventory in a warehouse?
Inventory in a warehouse is managed through systematic processes supported by WMS. This includes real-time tracking of stock levels, automating order processing, and employing inventory optimization strategies to maintain accurate and efficient inventory control.
What is the best software for warehouse management?
The best software for warehouse management depends on the specific needs of the business, including size, industry, and operational complexity. A comprehensive WMS that offers scalability, robust features, and integration capabilities is generally considered ideal and would be the best warehouse management software for your business operations.
How do you keep track of inventory in a warehouse?
Keeping track of inventory in a warehouse is typically done using a WMS, which may include technologies like barcoding, RF and RFID scanning, and IoT devices. These systems provide real-time updates on inventory levels and movements.
What is the most popular WMS?
The most popular WMS varies based on market segments and user needs. Popular systems are those that offer comprehensive features, scalability, and integration capabilities, like ASC Software’s WMS. The choice depends on the specific requirements and budget of the business.