A Master Production Schedule (MPS) outlines what products to make, in what quantities, and by when. It helps manufacturers meet market demand efficiently. But how do you create one effectively? In this article, we’ll define MPS, explore its key functions, and offer practical steps to implement and manage it.
Key Takeaways
- The Master Production Schedule (MPS) balances sales demand with manufacturing capacity, ensuring efficient production to meet market demands without overproducing or underproducing.
- Creating an effective MPS involves accurate product categorization, realistic lead time setting, and aligning resources with production rates to maintain a steady production flow.
- Implementing an MPS improves inventory control, enhances customer satisfaction by ensuring timely order fulfillment, and can integrate well with advanced technologies like AI and machine learning for better forecasting and dynamic scheduling.
Take Control of Your Shop Floor
From production scheduling to quality control, ASCTrac MES gives manufacturers the tools to optimize every step.
Request a Demo
Defining the Master Production Schedule (MPS)
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) is integral to production planning. It delineates the items to be produced, their quantities, and their production timelines. An accurate master production schedule ensures every cog in the manufacturing machine works in unison to meet market demand. The MPS isn’t just about listing production targets; it’s a sophisticated plan that includes time frames, manufacturing lead times, and the resources required to meet these targets.
Essentially, the MPS harmonizes sales demand with manufacturing capacity. This balance is vital; without it, companies risk either overproducing and incurring unnecessary costs or underproducing and missing out on potential sales. The MPS is not a static document but a dynamic plan that evolves with changing market conditions and internal capabilities. It considers various factors, including historical sales data, public demand assessments, and qualitative insights, to craft a roadmap that guides the entire production operation.
Depending on the industry and production cycles, the MPS planning horizon can span from a few months to several years. This long-term view helps companies prepare for future demands and align their resources accordingly. An accurate MPS is the result of meticulous planning and data analysis, ensuring that production flows smoothly and efficiently, meeting both current and future demands.
Core Functions of a Master Production Schedule
The Master Production Schedule (MPS) performs several key roles pivotal to effective production management. One of its primary roles is to link sales demand with manufacturing capacity, creating a balance between supply and demand. This balance is crucial in ensuring that customer orders are fulfilled without overburdening the production capacity.
The MPS plays a vital role in optimizing production flow and making the entire production process more streamlined and efficient. It has several essential functions, including:
- Troubleshooting production shortfalls by identifying potential issues early and allowing for timely interventions.
- Freeing up resources and increasing production rates.
- Optimizing production methods.
This proactive approach not only saves time but also creates space for scaling the manufacturing business. In essence, the MPS is a dynamic tool that continually adjusts to changes in demand or capacity, ensuring that production operations run smoothly and efficiently.
Translating Production Plans into Action
The conversion of high-level production plans into implementable schedules forms the basis of an MPS. The MPS takes broad production targets and breaks them down into specific numbers of items to be produced within a given time frame. This detailed breakdown ensures that every piece of machinery and equipment is utilized optimally, contributing to a smooth production flow.
By converting strategic plans into day-to-day operations, the MPS ensures that the shop floor operates like a well-oiled machine. This alignment is crucial for maintaining production efficiency and meeting delivery deadlines. The MPS not only outlines what needs to be done but also provides a clear roadmap on how to achieve these goals, ensuring that the entire production line works in harmony.
Evaluating Alternative Production Scenarios
A key part of master production scheduling involves assessing alternative production scenarios. This process involves:
- Assessing multiple manufacturing routes to determine the most efficient and cost-effective options.
- Considering various scenarios to identify potential problems.
- Ensuring that production quality is maintained while minimizing manufacturing costs.
By following these steps, the MPS helps optimize the production planning process and decision-making.
Advanced Planning and Scheduling (APS) software can significantly aid in this process by generating trial schedules and providing alternative routes for production. Engaging in scenario planning prepares the production team for various disruptions, ensuring that the MPS remains resilient and adaptable in the face of unexpected challenges.
Determining Capacity Requirements
Through rough-cut capacity planning, the MPS fundamentally serves to ascertain capacity requirements. This process forecasts the necessary resources—such as labor, machines, and materials—to meet production demands. By accurately assessing capacity requirements, companies can ensure that they have sufficient resources to meet demand, thereby increasing productivity and profitability.
Rough-cut capacity planning also helps in identifying potential capacity shortfalls and adjusting the MPS accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that production operations are not disrupted by unforeseen resource constraints, maintaining a steady production flow and ensuring timely delivery of products.
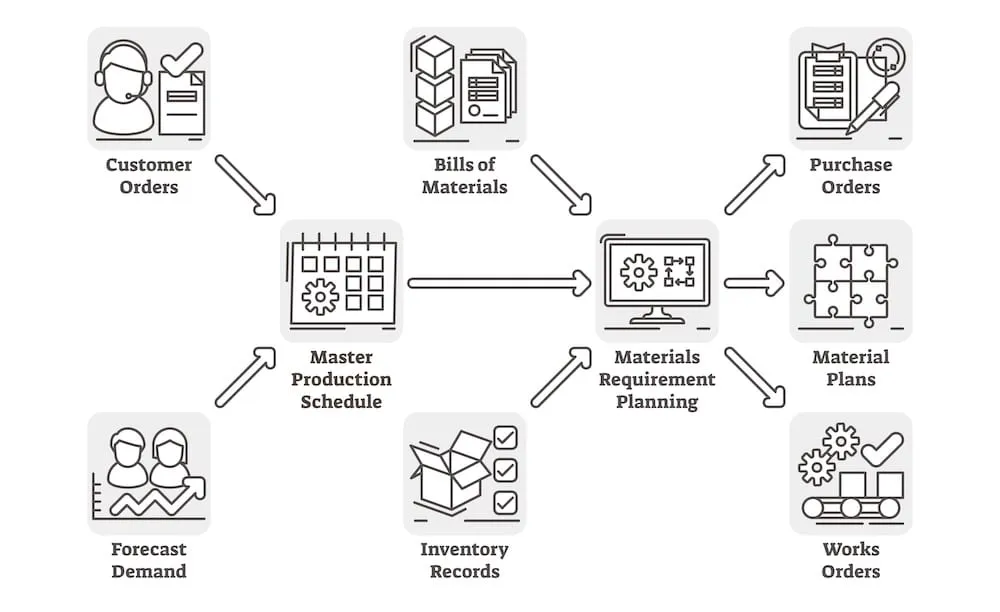
Key Components of a Master Production Schedule
An efficient production planning and execution process is guaranteed by the several key components that make up a Master Production Schedule. One of the primary components is demand forecasting, which uses historical sales data to project future demand accurately. This forecasting helps determine the required rate of production, ensuring that companies do not miss sales opportunities due to underproduction.
Another critical component is product categorization. Organizing products into specific categories and defining them clearly is essential for forming an accurate production calendar. This categorization includes creating product lists and variations, such as different SKUs for various sizes and colors. Accurate product definitions help in precise scheduling and resource allocation, making the entire production process more efficient.
Production quantities and lead times are also vital components of an MPS. Defining the number of units to be manufactured each week based on demand and inventory levels ensures that production aligns with market needs. Setting realistic lead times, which include the duration for material gathering, manufacturing, packaging, quality control, and delivery, is crucial for meeting customer expectations and maintaining operational efficiency.
Related: Mastering Manufacturing Production Scheduling
Steps to Create an Effective Master Production Schedule
Several critical steps go into creating an effective and feasible Master Production Schedule. The first step is to organize products into specific categories and define similar products to form product groups. Accurate product definitions are essential for forming strict categories, which in turn aid in precise scheduling and resource allocation.
The next step is to set realistic lead times. This involves:
- Calculating the time taken from order placement to customer delivery.
- Ensuring that the MPS is grounded in reality.
- Continuously assessing and adapting lead times to fine-tune processes and ensure accuracy.
Finally, evaluating the master production schedule proposal with rough-cut capacity planning ensures that the plan is feasible and can meet production demands. This step involves identifying production shortfalls and troubleshooting problem areas to maintain a steady production flow.
Define Your Products Accurately
Successful MPS hinges on accurate product definition. Defining products clearly and categorizing them into specific groups helps in precise scheduling and resource allocation. For instance, splitting product variations into different SKUs ensures that each variant is accounted for in the production schedule, reducing the risk of errors and inefficiencies.
Before crafting an MPS, it is essential to categorize products accurately. This process involves creating a detailed yet focused list of product groups with the smallest number of alternatives possible. Accurate product definitions and categorization not only streamline the production process but also enhance the overall efficiency of the manufacturing operation.
Set Realistic Lead Times
For timely delivery and enhanced customer satisfaction, it’s key to set realistic lead times. Accurate lead time calculations provide reliable delivery schedules to clients, enhancing customer trust and retention. Knowing the lead time for manufacturing a batch of products helps in maintaining operational metrics and meeting customer expectations.
Being realistic with lead times involves calculating the manufacturing lead time accurately to ensure deadlines are met. This calculation includes the duration for:
- Material gathering
- Manufacturing
- Packaging
- Quality control
- Delivery
Past experiences and manufacturing data are essential for determining lead times accurately, helping to avoid overscheduling and potential problems.
Align Resources with Production Rates
Maintaining a steady production flow and avoiding bottlenecks necessitates the alignment of raw materials, resources with production rates, while also considering production and maintenance costs. Assessing resource availability, such as machines and labor, helps ensure that production rates are aligned with demand. This alignment might require reallocating resources from lower-demand areas to meet higher demands, ensuring that critical production targets are met.
In some cases, expanding resource levels may be necessary to meet production rate targets. Ensuring that resources are not oversaturated helps maintain a steady production flow, making the entire production operation more efficient. Proper resource alignment also aids in better planning for hiring based on the projected labor needed, further enhancing production efficiency.
Tips for Managing a Master Production Schedule
To keep the schedule accurate and in line with business objectives, effective management of a Master Production Schedule (MPS) requires the application of several strategies. One of the key tips is to balance demand and supply, ensuring that the MPS delivers products efficiently and meets customer expectations. Regularly reviewing and updating the MPS based on real-time data helps maintain its accuracy and relevance.
Using master production scheduling software can automate many aspects of the MPS, making it easier to generate and adjust the schedule. Interactive schedule tools can display MPS data as stock profile graphs and capacity usage graphs, providing a visual representation of production metrics.
Collaborating across departments and integrating the MPS with ERP systems can also improve communication and ensure coordinated efforts.
Prioritize High-Demand Items
By prioritizing high-demand items in the MPS, timely delivery is ensured and customer satisfaction is enhanced. High-priority items should be listed at the top and given priority treatment in the production schedule. This focus helps in meeting customer expectations and maintaining high service levels.
Focusing on high-demand items first has several benefits:
- It optimizes resource utilization, ensuring that critical products are always available for customers.
- It helps to avoid stockouts and maintain a high rate of production to cater to demand.
- It ensures that high-demand products are readily available.
Break Down Tasks for Better Management
A practical strategy for better management of a Master Production Schedule is to break tasks down into smaller steps. By dividing tasks into manageable units, it becomes easier to:
- Estimate time requirements
- Manage workflows effectively
- Track progress
- Ensure that each step of the production process is completed efficiently.
Furthermore, breaking down tasks facilitates improved accountability among team members. When tasks are clearly defined and assigned, it is easier to monitor performance and ensure that everyone is contributing effectively to the overall production goals. This method enhances transparency and helps identify bottlenecks early, allowing for timely interventions to keep the production schedule on track.

How Manufacturers Utilize a Master Production Schedule
To streamline operations, boost efficiency and guarantee timely order fulfillment, manufacturers across a variety of industries employ Master Production Schedules. By integrating MPS with manufacturing ERP systems, companies can automate much of the scheduling process, reducing errors and enhancing responsiveness to changes in demand or supply. This automation is particularly beneficial in maintaining a steady production flow and avoiding bottlenecks.
Artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning (ML) further optimize MPS by enhancing forecast accuracy, automating dynamic scheduling, and facilitating real-time adjustments. These technologies help manufacturers anticipate market changes and adjust their production plans accordingly, ensuring that customer demands are met efficiently. Additionally, MPS can be used to calculate labor requirements and shifts many months in advance, aiding in better workforce planning.
Implementing an MPS fosters good business habits and prepares companies for scalability. By defining clear and measurable production objectives, manufacturers can focus on producing profitable goods and improving net revenue, net profits, and return on investment. MPS also integrates well with lean manufacturing principles, streamlining production processes, minimizing waste, and ensuring just-in-time delivery of products.
Benefits of Implementing a Master Production Schedule
Implementing a Master Production Schedule brings about numerous and significant benefits. One of the primary advantages is improved inventory control. An effective MPS helps determine and achieve desired inventory levels, avoiding both shortages and overstocking. This balance ensures that resources are used efficiently and reduces unnecessary production and storage costs.
Another significant benefit is increased customer satisfaction. By providing more accurate estimates of material requirements and delivery dates, the MPS ensures that customer orders are fulfilled on time. This reliability enhances customer trust and loyalty, contributing to the overall success of the business.
Additionally, the MPS helps reduce lead times throughout the year, making the production process more efficient and responsive to market demands.
Related: Guide to Material Requirements Planning (MRP): What it is and Why it’s Important
Common Challenges and Solutions in Master Production Scheduling
Master Production Scheduling comes with its own set of challenges. One common issue is handling demand variability, which can lead to overproduction or stockouts if not managed properly. Implementing safety stock levels can buffer against unexpected changes in demand, ensuring that production levels remain stable. Inaccurate sales forecasts also pose a significant challenge, disrupting the MPS and causing inefficiencies. To combat this, companies should gather high-quality data and continuously refine their forecasting methods.
Capacity constraints can hinder the execution of the MPS, leading to missed deadlines and unmet customer demands. Regular rough-cut capacity planning helps ensure that resources meet production demands, preventing such issues. Another tactic is to freeze the MPS for the initial few periods before production starts, preventing last-minute changes that could disrupt the schedule. By addressing these challenges proactively, companies can maintain a more accurate and efficient production schedule.
Examples of Master Production Schedules in Different Industries
Various industries attest to the adaptability and effectiveness of Master Production Schedules. In Make-to-Stock (MTS) industries, such as consumer electronics, MPS focuses on finishing the production of goods in anticipation of sales. This approach ensures that products are readily available for retail sales, reducing lead times and meeting customer demand promptly.
In contrast, Make-to-Order (MTO) industries, like custom furniture manufacturing, use MPS to tailor production processes to specific customer orders. Production begins only after orders are received, allowing for customization and ensuring that customer preferences are met. This flexibility helps in maintaining high service levels and customer satisfaction.
Various other industries implement MPS to streamline their production processes, reduce inventory costs, and enhance customer satisfaction. By aligning production schedules with market demands, MPS enables companies to optimize their operations and achieve better production planning outcomes.
How ASC Software Enhances Your Master Production Schedule (MPS)
A well-managed Master Production Schedule (MPS) is key to manufacturing success, but achieving efficiency requires the right tools. ASC Software’s integrated solutions streamline your MPS process, ensuring a balance between supply and demand while optimizing production flow. Here’s how we can help:
- Real-Time Inventory Control: With ASC Software’s Warehouse Management System (WMS), monitor your inventory in real-time to accurately forecast demand and prevent issues like overproduction or stockouts. This level of control is essential for maintaining a smooth and effective MPS.
- Automated Scheduling and Planning: Our Manufacturing Execution System (MES)/Material Requirements Planning (MRP) system works hand-in-hand with your MPS, automating production schedules to align with demand forecasts and capacity planning. This integration ensures that production processes are efficient and adaptable to changing needs.
- Data-Driven Decision Making: Our solutions provide robust analytics to monitor production performance, assess lead times, and align resources with demand. With these insights, you can fine-tune your MPS for enhanced efficiency and productivity.
- Seamless Integration: ASC Software’s solutions seamlessly integrate with your current systems, offering a unified platform for managing production. This comprehensive integration ensures that your MPS remains responsive to market shifts and production constraints.
Ready to optimize your Master Production Schedule? Discover how ASC Software can enhance your production planning.
Summary
In summary, a Master Production Schedule is an indispensable tool for managing product supply, balancing demand, and planning production processes. It translates high-level production plans into actionable schedules, evaluates alternative production scenarios, and determines capacity requirements to ensure efficient resource allocation and timely delivery. By accurately defining products, setting realistic lead times, and aligning resources with production rates, companies can create an effective MPS that enhances production efficiency and customer satisfaction.
Implementing an MPS brings numerous benefits, including improved inventory control, increased customer satisfaction, and efficient resource allocation. Despite common challenges such as demand variability and capacity constraints, proactive solutions like safety stock and regular capacity planning can help maintain a more accurate and efficient production schedule. Advanced tools, such as those offered by ASC Software, can further optimize your MPS, providing real-time inventory control, automated scheduling, and seamless integration with your current systems. By understanding and leveraging the core functions and key components of an MPS, manufacturers can streamline their operations, improve efficiency, and achieve better production planning outcomes.
Optimize Your Production with ASC Software
A successful Master Production Schedule requires the right tools to support your production goals. ASC Software’s comprehensive solutions are designed to streamline your MPS process, ensuring efficient inventory management, scheduling, and resource alignment. Ready to take your production planning to the next level? Contact us today to learn how ASC Software can enhance your MPS and drive operational efficiency.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is a Master Production Schedule (MPS)?
A Master Production Schedule (MPS) is a detailed plan that specifies the products to be produced, their quantities, and production timing, ensuring efficient supply and demand balance.
How does an MPS improve production efficiency?
An MPS improves production efficiency by optimizing production flow, ensuring timely delivery, and aligning resources with production rates. This leads to an overall improvement in efficiency.
What are the key components of an MPS?
The key components of an MPS include demand forecasting, product categorization, production quantities, and lead times. These elements are crucial for effective production planning.
How do manufacturers use MPS in different industries?
Manufacturers use MPS differently across industries, utilizing it to anticipate sales in Make-to-Stock industries and fulfill specific customer orders in Make-to-Order industries.
What are common challenges in MPS, and how can they be addressed?
Common challenges in MPS include demand variability and capacity constraints. These can be addressed through safety stock, refining forecasting methods, and regular capacity planning.




